YouTube rapidly evolved from a general entertainment platform into a powerful space for professional learning. Instructional technologists and educators can harness its video ecosystem to explore teaching innovations, classroom technology integration, and strategies for student engagement. By subscribing to reputable EdTech channels and using targeted keywords such as flipped classroom, digital storytelling, or project-based learning, educators can mine YouTube for diverse instructional models and real-world applications. The platform’s recommendation algorithm further supports professional learning by curating personalized content based on consistent, purposeful engagement (Alshalawi, 2022).
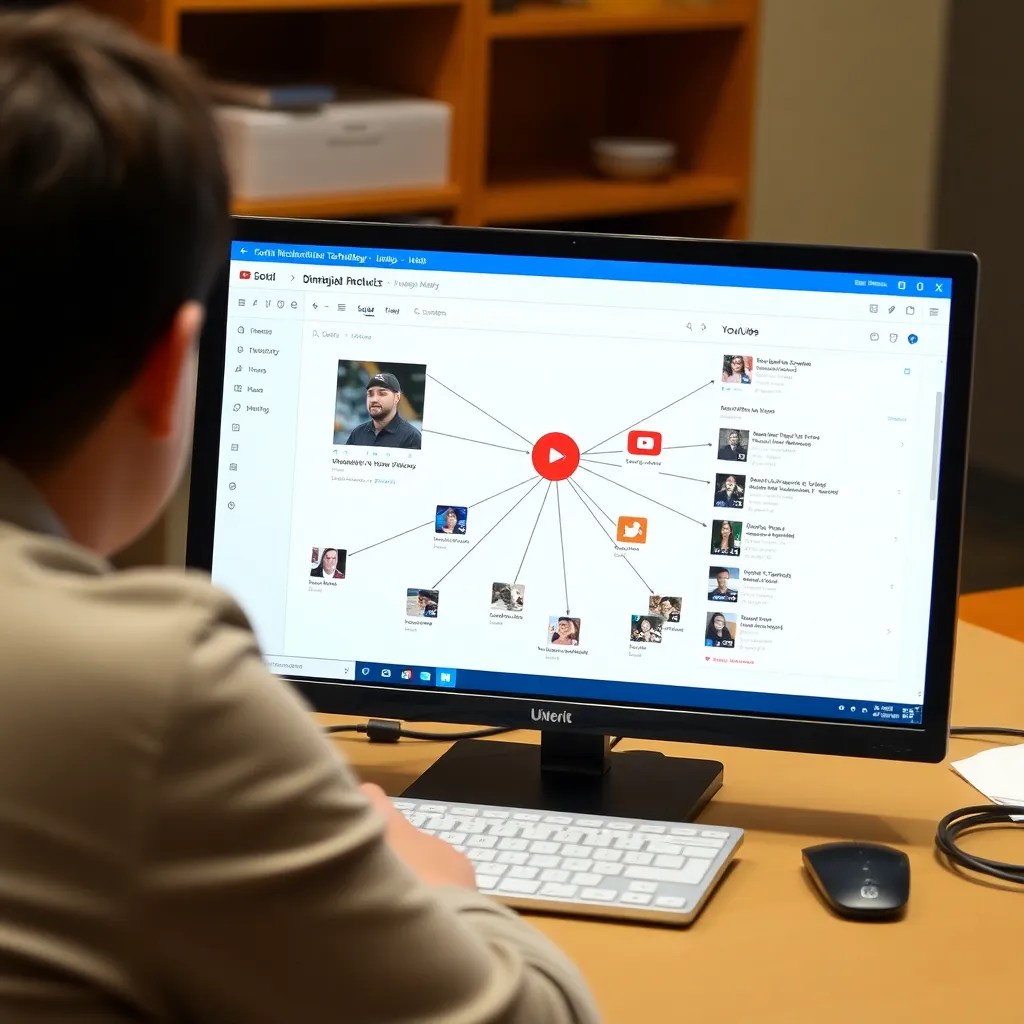
The accompanying infographic illustrates an organized approach to YouTube mining. It begins with keyword searches and channel vetting, followed by network mapping to identify key creators, collaborators, and professional learning communities. A credibility funnel ensures that educators assess content reliability by considering source expertise, evidence, engagement quality, and cross-verification.

Research indicates that microblogging-style platforms such as YouTube foster active knowledge exchange when users interact intentionally through subscriptions, playlists, and comments (García-Río, et al. 2022).

To maximize YouTube’s potential as a professional learning tool, educators should:
- Subscribe to curated channels and playlists for continuous updates.
- Engage thoughtfully in comments to exchange insights and grow professional networks.
- Evaluate video content systematically using the credibility funnel.
- Verify strategies through academic or professional sources before classroom implementation.
When mined thoughtfully, YouTube serves as a dynamic professional learning network, blending creativity, collaboration, and ongoing professional development.
The info graphic below
Reference
Alshalawi, A. S. (2022). The influence of social media networks on learning performance and students’ perceptions of their use in education: A literature review. Contemporary Educational Technology, 14(4), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.30935/cedtech/12164
García-Río, E., Baena-Luna, P., Palos-Sánchez, P., & Aguayo-Camacho, M. (2022). Microblogging: An online resource to support education and training processes. Campus Virtuales, 11(2), 39–48. https://doi.org/10.54988/cv.2022.2.1013
